Consulta por Variable
Ácidos ("Los limones están ácidos")
Agua
Año ("La niña tiene dos años")
Araña
Ayer
Brujería ("Brujo")
Cangrejo
Carga
Cigarro
Cinco
Danzantes ("Hay muchos danzantes")
De ellos ("La comida es de ellos")
Duermen (ellos/as), ("Duermen poco")
Duermes ("Duermes por la tarde")
Duermo ("Duermo en la tarde")
Duro
Escoba
Espeso ("El atol está espeso")
Está acostado ("El bebé está acostado")
Estamos acostados
Estás acostado
Haraganes ("Los muchachos son haraganes")
Hombres ("Los hombres ya trabajaron")
Iguana
Incienso/Copal
Jocote
Jóvenes ("Los muchachos trabajan")
Jugaron (ellos/as), ("Jugaron con el perro")
Ladrón
Le hablé ("Le hablé a mi abuela")
Le habló ("El niño le habló a su mamá")
Le pagó ("Mi abuelo le pagó al niño")
Le pegó ("El muchacho le pegó a la niña")
Lejos ("Mi casa está lejos")
Lo abrigó ("El niño se abrigó con la chamarra")
Lo agarra ("La niña agarra su cabeza")
Lo ayudo ("Ayudo a mi papá")
Lo buscará ("Buscará a tu mamá")
Lo empuja ("La niña empuja a su hermana")
Lo está agarrando ("El niño está agarrando zompopos")
Lo está esperando ("Está esperando a su papá")
Lo está viendo ("El señor está viendo a los niños")
Lo estoy usando ("Estoy usando el hacha")
Lo lavo ("Lavo mi ropa")
Lo tejió
Los ayudaré
Los buscará (ellos/as), ("Él señor los buscará")
Los empuja (Uds.), ("El niño los empuja")
Los está esperando (Uds.),("la abuela los está esperando")
Los está viendo (ellos/as)
Mapache
Masa
Me bañé
Me está viendo
Me estoy cambiando
Me orinó ("El perro me orinó")
Me pagó ("La señora me pagó ayer")
Mes ("Un mes")
Mi maíz
Mi papá
Mi pueblo
Mi uña
Mozo ("Tengo tres mozos")
Mucho
Mujeres
Nos buscará ("Ella nos buscará mañana")
Nos está esperando ("Mi hermano nos está esperando")
Nos está viendo ("La señora nos está viendo")
Nos estamos cambiando ("Nos estamos cambiando de ropa")
Nos hemos bañado ("Nosotros ya vamos bañado")
Nos pagó ("El muchacho nos pagó")
Nueras ("Las nueras ya se fueron")
Nuevo
Pequeños ("Las naranjas están pequeñas")
Pesado ("La piedra es pesada")
Pez, pescado
Piojo
Ropa ("Tendí la ropa")
Saliva
Sangre
Se bañó ("Él ya se bañó")
Se están cambiando (ellos/as)
Se están cambiando (Uds.), ("Ustedes se están cambiando de zapato")
Se han bañado (ellos/as), ("Ellos ya van bañados")
Se han bañado (Uds.), ("Ya van bañados")
Se levantará
Se levantarán (ellos/as)
Señoritas ("Las señoritas están platicando"), ("Las niñas están jugando")
Su casa ("La casa de mi abuela")
Su pueblo ("El señor llegó a su pueblo"
Sustituto ("Encontramos tu sustituto")
Te buscará
Te está esperando ("Tu papá te está esperando")
Te estás cambiando
Trabajaste ("Trabajaste poco")
Zapote
Zopilote, zope
¿Cómo?
¿Con quién?
¿Cuándo? ("¿Cuándo vienes?")
¿Cuánto? ("¿Cuánto cuesta la piña?")
¿Dónde?
¿Por qué? ("¿Por qué trabajas de noche?")
¿Qué?
¿Quién?, ("¿Quién vino?")
A pie
Abierto
Abuela
Abuela/madre luna
Abuelas/ancianas
Abuelo
Adornar ("Adorné mi casa")
Agachado
Aguacate
Aguado ("La masa está aguada")
Agujero/zanja ("El señor hizo una zanja/agujero")
Al lado de
Ala
Algodón
Algún día
Allá ("Allá está el pueblo")
Almohada
Amarrado
Amontonado ("La basura está amontonada")
Ampolla
Anteayer ("Estuvo lloviendo anteayer")
Antes, hace tiempo
Aparecer ("Apareció un arcoíris")
Aquí ("Aquí hace frío")
Árbol
Árbol de izote
Árbol de pito ("Corté un árbol de pito")
Arete
Armadillo
Arrugado ("La camisa está arrugada")
Áspero
Atol
Atrevido ("El muchacho es atrevido")
Aun no, todavía no
Avispa ("Hay muchas avispas")
Azadón
Azúcar
Babosa
Balanza, pesa
Banano
Bebé
Bien/Bueno ("Hizo muy bien el trabajo")
Bisnieto
Blusa
Boda, casamiento
Bofetear ("Al muchacho le dieron una bofetada")
Bonito
Bote para basura
Burro (animal)
Cabello ("Me corté el cabello")
Calambre
Calcetín
Calvo/pelón
Cama ("Ensució la cama")
Camino
Campo, terreno para labrar la tierra
Canasto
Cántaro/vasija
Cárcel ("El señor fue a la cárcel")
Carne
Caspa
Cebolla
Ceguera ("El señor está ciego", "Me quedé ciego")
Cementerio
Cerdo/marrano
Cerrar
Chicle
Chile
Chipilín
Chompipe
Cielo
Cintura
Coche de monte
Coco
Codo
Collar
Colocho
Columna, horcón, paral
Columpio
Comilón ("El niño es comilón")
Concha
Conejo
Corre
Cortar (con cuchillo o machete)
Corto
Cosquillas
Creador y formador (Dios)
Cuchillo
Cuervo
Cuña
Cutete
De repente
De una vez, en este momento
Debajo de ("El gato está debajo de la mesa")
Delgado (objeto)
Derretir
Descortezar, quitar corteza de árbol
Descosido (prenda de vestir)
Desnudo
Despacio
Deteriorado, podrido
Diarrea
Diente
Difícil ("La rama está difícil de quebrar", "El trabajo está difícil")
Dinero
Dolor
Dormimos ("Nos dormimos hasta medianoche")
Duerme ("El bebé duerme con su madre")
Duermen (Uds.), ("Duermen mucho")
Ejote
El único
Embrocado
Empapado, bien mojado
Encima de ("El gato duerme encima de la silla")
Encorvado
Enderezar
Enojado
Enrollar
Entreabierto (puerta)
Escritura ("El niño ya escribe")
Escudilla ("El caldo lo dieron en escudilla")
Escuela
Eso, esa
Esponjoso parecido al peluche
Está agonizando
Están acostados (Uds.)
Están Costados (Ellos/as), ("Están acostados sobre la cama")
Este ("Este perro", "Esta mesa", "Esta Silla")
Estiércol, popó
Estornudo ("El señor estornudó")
Estoy acostado
Estrecho, ajustado ("El camino está estrecho", "La camisa me queda apretada")
Estrella
Faja para mujer
Feo
Flauta
Flautista
Flojo
Flor
Flor de izote
Flor de pito
Fruta
Gallina chaparra
Gallina clueca
Gallo
Gemelo
Golpe
Gorro
Gota
Grandes ("Las frutas están grandes")
Grieta en el talón ("Tengo grietas en los talones")
Gris ("El pollo es de color gris")
Gruesos ("Las tortillas están gruesas")
Grupo
Guía, cofrade
Güisquil
Gusano
Gusano chichicaste
Hace rato
Hedor/pestilencia ("El perro apesta")
Hinchazón
Hipo ("Me dio hipo")
Hongo
Hoy
Hule/honda ("Hice una onda", "Mis zapatos son de hule"
Incensario
Ingrediente ("Traje los ingredientes para los tamales")
Inútil
Invierno
Jiote ("El perro tiene jiote")
Jugamos ("Nosotros jugamos ayer")
Jugaron (Uds.), ("Ustedes jugaron ayer")
La mitad
Lagartija
Lapicero/lápiz ("El niño escribe con lápiz")
Lazo
Le habló ("El niño le habló a su abuelo")
Le pegué ("Le pegué en la mano")
Les pagó (ellos/as), ("Mi mamá les pagó")
Les pagó (Uds.), ("Mi papá les pagó")
Limpio
Líquido o jugo
Llevado de la mano
Llovizna
Lo apretó
Lo asó ("Mi mamá asó carne")
Lo busca ("El niño busca su ropa")
Lo cantó
Lo chupa ("El niño chupa un limón")
Lo colgó ("Mi abuelo colgó su camisa")
Lo comprará ("Mi mamá comprará la comida", "Ella comprará la tortilla")
Lo defecó ("El gato defecó las plantas")
Lo deseo
Lo encaló ("Mi papá encaló el árbol")
Lo enfría ("El señor enfría su comida")
Lo envuelve
Lo estoy agarrando
Lo estoy quebrando ("Estoy quebrando piedra")
Lo hizo ("Mi papá hizo una casa")
Lo lava ("La señora lava la calle", "Lava su ropa")
Lo pensé
Lo picoteó ("El gallo lo picoteó")
Lo pisa ("La niña pisa la basura")
Lo probó
Lo restregué (ropa)
Lo secó
Lo soltó
Lo vació
Lo venderá ("Mi hermana venderá los aguacates")
Lo venderé ("Venderé mi casa")
Loro
Los buscará (Uds.), ("Él los buscará mañana")
Los empuja (ellos/as), ("La niña los empuja")
Los está esperando (ellos/as), ("Mi abuelo los está esperando")
Los está viendo (Uds.) ("La señora los está viendo")
Luciérnaga
Lugar ("El joven se cambió de lugar")
Lunar
Machucado ("Me vendieron tomate machucado")
Madera
Madrugaste o amaneciste.
Mal hecho
Mandíbula/quijada ("Me duele la mandíbula")
Manteca/aceite ("Usé manteca para los tamales")
Mar
Marimba
Mariposa
Matorral, monte
Me buscará
Me empuja ("El viento me empuja")
Me está esperando ("Mi papá me está esperando")
Me he bañado ("Ya voy bañado")
Me levantaré
Me picó
Me puso de lado
Mecapal
Medianoche
Mejillas grandes
Mestizo o ladino
Mi amigo ("El perro es mi amigo")
Mi casa
Mi cuerpo
Mi hijo
Mi pie
Miltomate
Moco ("El niño está sacando moco")
Moho
Mojado
Mojarra
Moler
Mono/mico
Morder
Morral, matate
Morro, jícara
Mosca verde
Mosquito
Mosquito arador
Muchas cosas
Mudo
Muertos ("Hubieron muchos muertos", "Encontraron varios muertos")
Mugre
Mujer
Nacedero de agua
Nada ("No hay nada")
Naranja
Neblina ("Bajó mucha neblina")
Negro
Nido
Nieto
Nigua
No
No es posible o no creo
No hay ("No hay dinero")
Nopal
Nos empuja
Nos levantaremos
Nuestro padre sol
Nuestro, de nosotros
Nunca
Obeso, gordo
Ojos cerrados
Olla
Oloroso
Olote/xilote
Olvidadizo
Ombligo
Orgulloso ("Él es orgulloso")
Orina
Oscuridad
Otra vez
Oveja o cabra
Pájaro
Pájaro carpintero
Pájaro piscoy ("Vi un pájaro piscoy")
Pálido ("La ropa se ve pálida")
Paloma silvestre
Palomilla de zompopo
Pañal
Pared
Pedro
Pegajoso
Peine
Pepita de ayote
Pequeño
Perniabierto
Persona mayor de baja estatura
Petate
Pez pupo
Piedra pómez ("Limpié el metal con una piedra pómez")
Piel
Piña, piñuela (piña pequeña)
Piojillo ("Las gallinas tienen piojillo")
Podrido por la polilla
Poner a cocer
Preso
Primero ("el niño llegó primero")
Pulga ("El perro tiene pulgas")
Puntiagudo
Pupo, tepocate, renacuajo
Putrefacto (alimento, comida o ser vivo)
Quédese
Rajado (leña)
Rana
Rápido
Rayo, relámpago
Red ("Una red de mazorcas")
Regañar
Rico, adinerado
Rodilla ("Mi rodilla")
Rojo
Ronrón ("Yo jugué con ronrones")
Ropa interior
Roto (ropa)
Sabiduría/consejo ("El abuelo es sabio", "El abuelo da consejos")
Sábila
Saco
Saltamontes, grillo
Sandía
Sapo
Se aclaró ("Se aclaró dentro de la casa")
Se arruina
Se asombró
Se cae
Se está cambiando ("La niña se está cambiando")
Se ha bañado ("´Él ya va bañado")
Se levantarán (Uds.)
Se pone ronco
Se raspó la mano
Se regresó
Sentado ("La señora está sentada")
Servilleta
Sí
Siempre
Silla
Sin permiso/en secreto ("Se fue a pasear en secreto", "Las señoritas hablaron en secreto")
Solo
Soñar
Sonreír ("La niña sonríe con su papá")
Soplador
Sordo
Su espuma ("Hay espuma en el agua")
Su frente ("El bebé se golpeó la frente")
Su hijo ("Mi hermana tiene dos hijos")
Su maíz ("Mi abuela compró su maíz")
Su papá ("El papá de la niña está trabajando"
Su vapor
Suave
Tacaño
También
Tapar/cubrir ("Tapé mi comida")
Te bañaste ("Te bañaste por la mañana")
Te empuja ("Mi hermano te empuja", "El viento te empuja")
Te está viendo ("El niño te está viendo")
Te has bañado ("Ya vas bañado")
Te levantarás
Te pagó ("A ti te pagó el señor")
Te quiere
Tecomate
Tejido ("Es grande la telaraña")
Temblor
Temprano
Termina ("La señora terminó su venta")
Tía
Tibio
Tiembla de frío
Tigre, jaguar
Tijera
Tinaja de barro o de plástico.
Tío
Tobillo
Tocoyal, tun
Tomate
Tonto
Torcido
Torcido ("El camino está torcido")
Tornado o remolino
Tortilla de maíz negro
Tostado (granos)
Trabajamos ("Trabajamos ayer")
Trabajaron (Ellos/as), ("Ellos trabajaron toda la semana")
Trabajaron (Uds.), ("Ustedes trabajaron en mi casa")
Trabajé ("Trabajé mucho")
Trabajó ("El señor trabajó en su pueblo")
Trenza
Trompo
Tronco
Tu mentira
Un manojo
Un pedazo ("Regáleme un pedazo de lazo", "Pásame un pedazo de tortilla")
Un poco
Ustedes
Vaca
Velo
Venado
Verde
Viejo, inservible
Viento
Viga ("Se cayó la viga", "Mi casa tiene varias vigas")
Y
Ya no
Yagual ("La señora usa su yagual para su carga")
Yegua
Zacate
Zanate
Zancudo
Zorrillo ("Los zorrillos apestan")
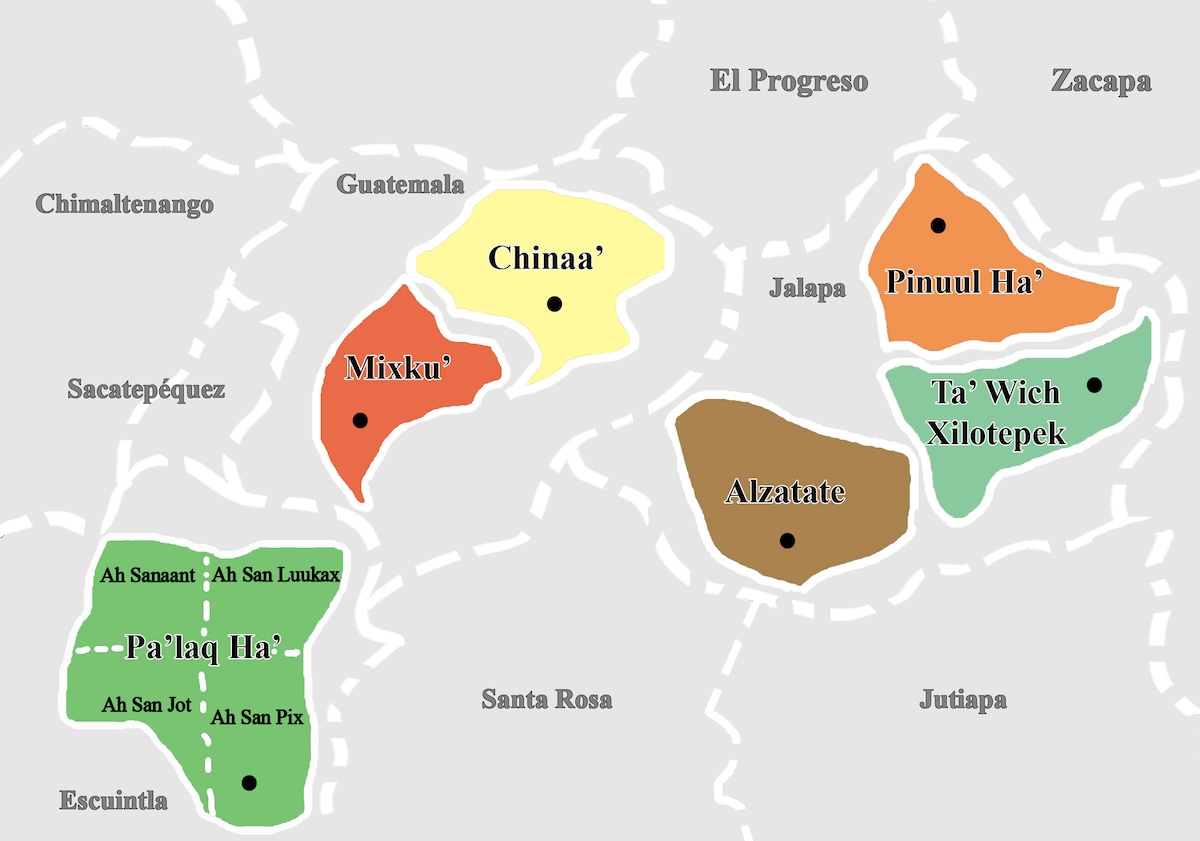
Consulta por Lugar
Pa'laq Ha'
Mixku'
Chinaa'
Alzatate
Pinuul Ha'
Ta' Wich Xilotepek